
EST November 5, the United States held the 60th presidential election, at the same time all 435 seats in the House of Representatives and 34 seats in the Senate will also be re-elected. The current U.S. presidential election is the most anxious election in recent years, according to a number of U.S. media the latest published calculations, the U.S. Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump locked in this U.S. presidential election victory, Trump has been declared the winner of the presidential election in 2024. In the congressional elections, the Republican Party will gain at least 51 Senate seats, enough to gain control of the Senate, the House of Representatives election Republican Party is temporarily ahead, but the result is variable. Trump's policy path is more unpredictable than Harris's, making him an important economic, political, and geopolitical variable for the U.S. and globally.
Figure 1 Map of the 2024 U.S. Election
Data source: Associated Press

Trump's election becomes a new variable in the U.S. economy as economic uncertainty rises
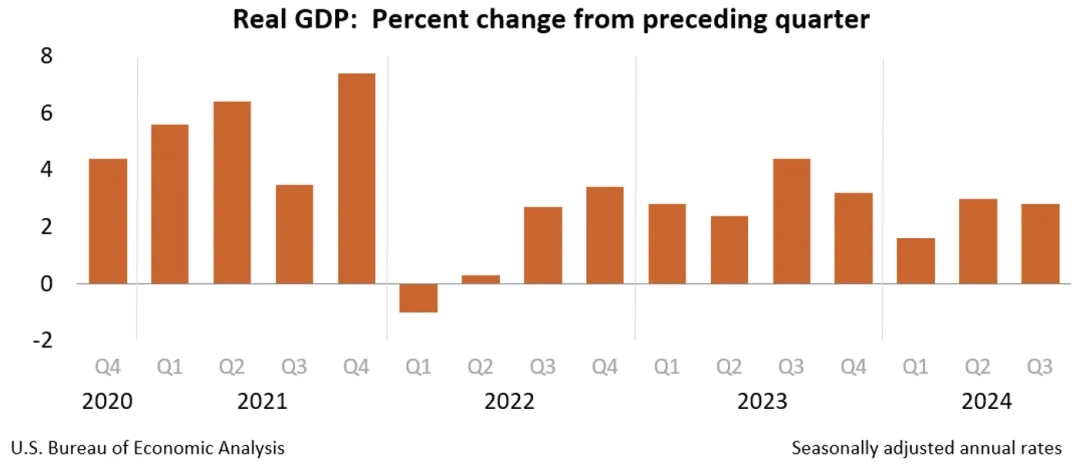
Trump advocates dovish policies or a short-term boost to the economy, but part of the effect may be offset by trade protection and restrictive immigration policies, inflation risk re-emergence or lead to interest rate levels in the longer term to remain high, increasing the uncertainty of the U.S. economy. Since the beginning of the year, the U.S. economy has shown strong resilience, and inflationary pressures have eased under persistently high interest rates, providing some cushion for the Fed to cut interest rates. the U.S. Consumer Price Index CPI rose 2.4% year-on-year in September, the smallest increase since February 2021. Although the volatility of employment data for the market to form a certain disturbance, but the overall view of the labor market shows a moderate slowdown trend, the U.S. unemployment rate has risen from 3.7% in early 2024 to 4.1% in September. According to the Federal Reserve's October forecast, the median forecast for the unemployment rate at the end of this year is 4.4%, higher than the 4.0% forecast in June. In the context of increasing downward pressure on the U.S. economy, in September 2024, the Federal Reserve lowered the target range for the federal funds rate by 50 basis points [1] to start a new cycle with aggressive rate cuts, and it is expected that the probability of the Federal Reserve lowering interest rates by 25 basis points in November and December, respectively, is higher. Prolonged high interest rates pose extensive risks to fiscal debt, the banking sector, etc., and inhibit the economy, and U.S. economic growth is expected to slow slightly to 2.7% in 2024.
Trump advocates dovish policies, including large-scale tax cuts [2], the commitment to increase domestic oil and natural gas production by easing restrictions on fossil fuels, while increasing investment in infrastructure and defense, or the short-term economic boost, but in this context the risk of U.S. inflation or the re-emergence of the rise in tariffs triggered by the trade protection policy will further push up inflation, which may result in the Federal Reserve's follow-up monetary policy The path of the Fed's subsequent monetary policy will be more variable. Superimposed on rising global geopolitical risks, intensifying trade frictions and restrictive immigration policies, the U.S. economy is facing high uncertainty, and the economic slowdown trend may be difficult to reverse, and economic growth is expected to slow down to less than 2.5% in 2025, and the subsequent trend will still depend mainly on the evolution of economic policies, Federal Reserve resolutions and geopolitical risks.
Figure 2 U.S. Quarterly Economic Trend (%)
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, U.S. Department of Commerce
U.S. Debt Sustainability Risks Rise as Tax Cuts Weaken Fiscal Base
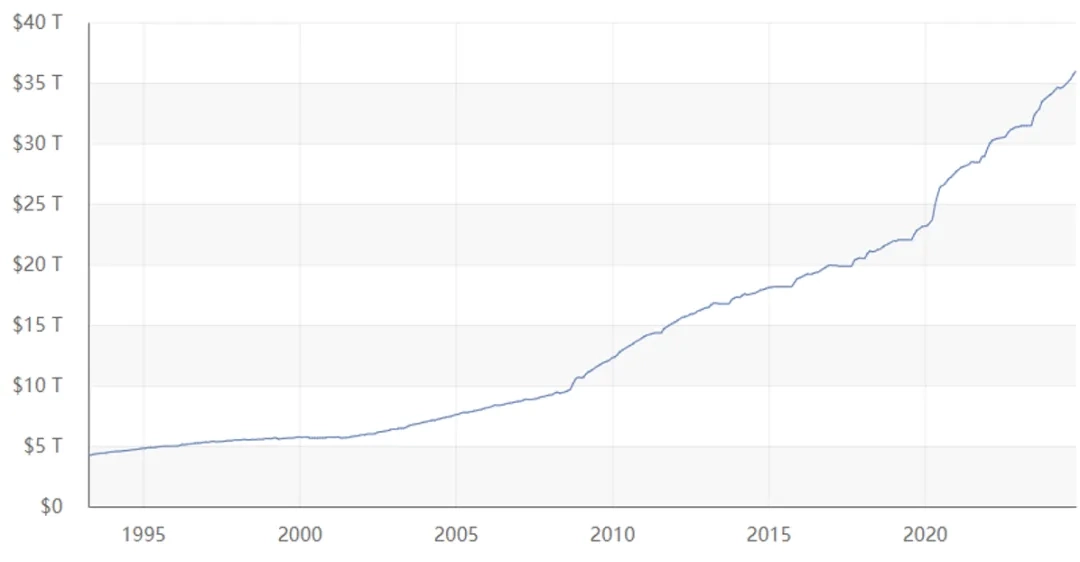
The tax cut policy advocated by Trump may further push up the debt, and under the expectation of high inflation, the downward speed of interest rates may slow down, and the high cost of debt increases the long-term fiscal risk of the U.S. The weakening of the fiscal strength has become a key factor in restricting the improvement of the U.S. sovereign credit level. The U.S. debt level is at the highest level among countries in the same class, and before the outbreak of the new crown epidemic, the U.S. fiscal deficit and debt level were already on an upward path. the U.S. government's fiscal deficit rate exceeded 7% in FY2023, and the government debt ratio[3] was about 109%, which is at a very high level. As of November 1, 2024, the stock of federal government debt has exceeded $35.8 trillion and is on an accelerated upward path since the suspension of the debt ceiling constraint. The fiscal policy advocated by Trump, which consists of lowering the corporate and personal income tax rates and setting higher spending levels, including increased infrastructure and defense spending, may lead to a further upward trend in government deficits and indebtedness, and, in the absence of substantive reforms, the fiscal deficit rate is expected to remain at a high level of more than 7% over the medium term, and the government's indebtedness may rise to more than 110%. According to the Federal Budget Accountability Board, an independent U.S. research organization, Trump's plan will lead to an increase in government debt of $7.5 trillion over 10 years, or $15.15 trillion in the worst-case scenario, based on medium-cost estimates.
At the same time, high interest rates have led to a significant rise in the cost of government debt and a steady decline in debt sustainability against a backdrop of a lack of credible fiscal consolidation by the government. a prolonged period of high interest rates since 2022 has dramatically raised the cost of U.S. government debt, with interest payments on the U.S. government's public debt reaching $1.1 trillion in FY2024, a 29 percent year-over-year increase from FY2023. Trump's advocacy of stimulative policies or push up inflation expectations, resulting in a slower pace of interest rates downward, and due to the cost of the national debt there is a certain lag, it is expected that the proportion of interest payments in fiscal year 2025 ~ 2026 will remain high, negatively affecting the sustainability of the debt. Against the backdrop of an economic slowdown, rising debt costs overlaid on an excessive debt burden will drive refinancing risk to the upside. When the debt ceiling negotiations restart in 2025, the federal government's total debt could reach $40 trillion, when the bipartisan game will face greater challenges.
Figure 3 Total U.S. Federal Government Debt (Trillions of Dollars)
Source: U.S. Department of the Treasury
Political party games escalate, social divisions intensify in post-election period
The escalation of the complexity of bipartisan tug-of-war in the United States poses a negative impact on the effectiveness and continuity of policies. Trump's governing style has intensified conflicts between different social groups and expanded partisan rivalries, and the potential for post-election popular protests and conflicts may result in increased divisions in American society. In recent years, political differences between the two parties in the United States have led to reduced legislative efficiency, weakening the ability of U.S. policymakers to plan substantive changes in policy, and the two-party game has repeatedly resulted in government shutdowns.2024 U.S. presidential election is the closest election in history in terms of candidate polls, and the campaign for this election involves a large amount of financial investment, increasing the influence of capital in politics, and due to the U.S. federal-state election system that resulted in an unbalanced distribution of resources and attention, both Democrats and Republicans filed a large number of lawsuits in swing states over voting eligibility, rules, and other details in the final stretch of the campaign. In terms of immigration policy, politicians from both parties have continued to polarize and antagonize the issue of immigration for electoral gain, with the laying of barbed wire at the border and the transshipment of immigrants epitomizing partisan bickering in the United States.
From the Capitol Hill riots to the attack on Trump, the intensification of political violence in the United States in recent years has shown that politicians of both parties and the public have serious differences on numerous issues [4], and the results of the general election in recent years have often been accompanied by controversy, which further deepens the public's skepticism about the fairness and transparency of the election. In this context, the potential for post-election public protests and violent conflict will not only affect social stability, but may also exacerbate political polarization in the U.S. and shake the public's trust in the government's ability to govern. In addition, political differences between the two parties have increased the difficulty of the U.S. government in resolving the debt ceiling issue, leading to increased uncertainty in policymaking and the legislature. The debt ceiling issue has deviated from the original intention of limiting the debt of the United States federal Government, and the debt ceiling negotiations have become a political showcase for the two parties to compete for votes and seek partisan interests.
Foreign Policy Emphasis on “America First” May Rewrite Global Geopolitical Direction
Trump's rise to power will intensify the unilateralist strategy of “America First”, reshaping the global geopolitical and economic order and increasing the unpredictability of foreign policy. The United States foreign policy differences between the two parties, the Democratic Party is committed to repairing and strengthening relations with traditional allies, the importance of multilateral alliances such as NATO, and support for the maintenance of international order through international organizations and multilateral agreements; while Trump seeks to return to the policy of “America First” to accelerate the flow of global capital and industry back to reshape the international geopolitical and trade patterns. Trump also advocates the return of “America First” policies. At the same time, Trump advocates reducing U.S. military involvement in international conflicts, asking allies to increase defense spending, and ensuring that other NATO members increase defense spending to at least 2% of GDP. The U.S. election is a key variable affecting the global geopolitical direction, especially the Russian-Ukrainian and Palestinian-Israeli situations. Trump has promised to end the Russia-Ukraine war and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict after his election, but if Trump adheres to the previous Middle East policy line, the implementation of the “Israel first” policy, including the comprehensive containment of Iran and the continuation of the creation of the civil unrest in Syria, it may aggravate tensions in the Palestinian region and further complicate the geopolitical situation in the Middle East. Trump on the U.S. aid to Ukraine is questionable, that should be left to Europe, and plans to “freeze” the Russia-Ukraine conflict before January 2025 through negotiations with Russia. If Trump is elected, Russia's existing control over Ukrainian territory will probably be recognized, Russia and Ukraine may be the fact that the occupied land as the border and achieve a ceasefire. In terms of China policy, the two parties in the United States have formed a high degree of consensus on the issue of China, and the results of the election will not reverse the U.S. competition-oriented policy tone. There is a high probability that Trump will restart the trade war with China after taking office, containing China through high tariffs and precise technological blockades. Compared to the Democrats, Trump advocates a more confrontational and unpredictable policy toward China. Overall, Trump's foreign policy emphasizes U.S. interests, weakens traditional alliances and multilateral cooperation mechanisms, and increases global geopolitical uncertainty and risk.
Short-term or support dollar strength, long-term strong dollar unsustainable
The deterioration of the financial strength of the United States and the continuous breakthrough in the upward movement of debt is eroding the credit base of the dollar, and the strong dollar may be difficult to sustain. In the short term, Trump's rise to power will support a strong dollar, but in the context of accelerating reverse globalization, slowing U.S. economic growth, and intensifying domestic political divisions, the accelerating upward movement of debt as well as rising costs have led to a steady decline in U.S. debt sustainability, which has had a certain impact on the status of the U.S. dollar and U.S. debt as a safe asset. Currently, benefiting from the current stage of the U.S. dollar and U.S. debt in the global financial system is at the heart of the U.S. government's debt sustainability is relatively high, the U.S. dollar as the world's most widely held reserve currency, the short term has not been replaced by the possibility of the leading position has been somewhat down [5]. Accompanied by the opening of the Federal Reserve's interest rate reduction cycle in September 2024, the dollar index has declined from a high level to the level of early 2022, and expansionary fiscal policy will push up U.S. bond yields, and the attractiveness of U.S. bonds may decline in the medium term. In addition, after Trump came to power, the trend of “anti-globalization” will further intensify, or lead to a decline in the demand for the dollar in the world. In the longer term, the deterioration of the U.S. fiscal strength, the debt ceiling will continue to break through the erosion of the dollar's credit base, along with the relative weakening of the U.S. geopolitical position and the increase in demand for non-dollar currencies in other economies, the dollar's international status will be weakened.
[1] The Federal Reserve has maintained the target range for the federal funds rate between 5.25% and 5.5% since July 2023, and on September 18, 2024, the Federal Reserve lowered the target range for the federal funds rate by 50 basis points to a range of 4.75% to 5% for the first rate cut by the Federal Reserve since March 2020, a rate cut that exceeded the general expectations of institutions.
[2] Trump proposes to further reduce the corporate tax rate from 21% to 15% and plans to extend and expand the 2017 personal income tax cut to increase disposable income for residents.
[3] The U.S. general government debt ratio is the combined public debt of the U.S. federal and local governments as a percentage of GDP.
[4] Democrats and Republican support groups have clearly divergent positions on issues such as race, immigration, climate policy, health care, and gun control.
[5] Over the past 20 years, the United States dollar's share of global reserve currencies has declined from 72% to less than 60%.







