
Xue Dongyang Chief Human Resources Officer of China Chengxin International and President of CCXGF
In order to thoroughly implement the spirit of the Central Financial Work Conference and the "Several Opinions of the State Council on Strengthening Supervision to Prevent Risks and Promote High-quality Development of the Capital Market", implement the requirements of the "Opinions on Strengthening Supervision of Listed Companies (Trial)" and other policy documents of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, promote the high-quality development of listed companies and enhance investment value, and standardize the disclosure of information related to the sustainable development of listed companies, under the guidance of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, on April 12, 2024, the three major exchanges officially issued the "Guidelines for Self-discipline/Continuous Supervision of Listed Companies - Sustainable Development Report (Trial)" (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines"), which will take effect on May 1, 2024. The release of the "Guidelines" has made clear regulations on the disclosure of sustainable information such as environmental, social and governance (ESG) by listed companies in China, filling the gap in the ESG information disclosure standards at the regulatory level of listed companies in China.
The standardization, consistency, comparability and authenticity of listed companies in the disclosure of sustainable development information not only lays the foundation for the credibility of ESG ratings, but is also a key factor in effectively attracting long-term investment capital. Through a comprehensive analysis of the sample companies of the SSE 180, Science and Technology Innovation 50, Shenzhen 100, and ChiNext indices that are included in the mandatory disclosure of the Guidelines, as well as companies listed at home and abroad (hereinafter referred to as "mandatory disclosure sample companies"), it is found that the disclosure ratio of mandatory disclosure sample companies has steadily increased in the past three years, and the overall disclosure ratio in 2024 is nearly 91%; ESG ratings have steadily improved, and the proportion of A (inclusive) and above has remained at around 63% in the past two years.
The ESG disclosure and rating performance of the mandatory sample companies has played a good social demonstration effect, which will further enhance the standardization and enthusiasm of information disclosure by listed companies and even relevant corporate entities in the entire market. In particular, with the release of the "Corporate Sustainability Disclosure Standards - Basic Standards" (Draft for Comments) (hereinafter referred to as the "Basic Standards") by the Ministry of Finance on May 27, 2024, the "dual importance" principle has increasingly higher substantive requirements for ESG information disclosure, and companies should make preparations and plans in advance to cope with more stringent regulatory requirements.
1. The impact of strong regulatory ESG information disclosure policies on corporate sustainable development
International ESG developed earlier, and there are relatively more ESG information disclosure standards. In recent years, they have gradually become integrated. Faced with many international disclosure standards, companies are at a loss. Domestic ESG information disclosure standards are mostly presented in the form of group standards and research projects, which pose certain challenges in terms of authority and applicability. The introduction of ESG information disclosure standards at the regulatory level in my country has always been the expectation of various organizations and companies, and has injected a shot in the arm for Chinese companies.
After years of exploration, sedimentation and accumulation, my country's ESG information disclosure has gradually evolved from exploration to standardized development. The three major exchanges under the guidance of the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council and the China Securities Regulatory Commission and the Ministry of Finance have respectively issued ESG supervision and promotion policies at different levels from 2022 to 2024. As of now, my country has formed a framework for mandatory ESG information disclosure at the national and regulatory levels. The effective implementation of the "Guidelines" of the three major exchanges, as an important document officially issued at the regulatory level with practical guidance value for ESG information disclosure, is also a focus of attention for listed companies in the capital market and other social enterprises.
1. It fills the gap in ESG information disclosure standards at the regulatory level of listed companies in my country and contributes to the normalization and standardization of ESG information disclosure
As the first domestic ESG information disclosure standard document at the regulatory level, the "Guidelines" have six chapters and 63 articles. They provide detailed descriptions of the four core content disclosure frameworks, including the scope of application of the "Guidelines", implementation time, disclosure requirements, transitional arrangements, "governance - strategy - impact, risk and opportunity management - indicators and targets", as well as disclosure information on 21 topics including climate change response, pollutant emissions, ecosystem and biodiversity protection, rural revitalization, innovation-driven, employees, etc. It provides a comprehensive reference for companies to conduct ESG information disclosure, and is both practical and normative.
(II) Complying with the “dual importance” principle, higher requirements are placed on corporate ESG information disclosure. The first batch of sample companies that are required to disclose ESG information face higher challenges.
Both the Guidelines and the Basic Standards set forth regulations and requirements for the ESG information disclosure of enterprises from the perspectives of "financial importance" and "impact importance", combining dual importance with the actual development of enterprises, and differentiating the content of enterprise disclosure, which is more scientific and reasonable. However, from the essence of "dual importance", enterprises are not only required to combine ESG issues with their own financial indicators, but also pay attention to the impact of enterprise development on the external environment. How to measure, evaluate and disclose in a quantitative way has become a key and difficult point in enterprise information disclosure. For the sample companies of the SSE 180, Science and Technology Innovation 50, Shenzhen 100, and ChiNext indices that are included in the mandatory disclosure of the Guidelines, as well as domestic and overseas listed companies, how to effectively implement the disclosure requirements in 2026 is an important challenge.
(III) Regulatory guidelines promote the healthy and sustainable development of the ESG ecosystem, including ESG ratings
As an important participant in the development of the ESG ecosystem, the regulatory body provides a standardized standard for the development of the ecosystem through policy formulation, which helps promote other participants to better apply ESG disclosure information. Enterprises are the main body of information disclosure. Information transparency and the substance of disclosed information are the basis for ESG rating of enterprises. The dual importance principle is consistent with the connotation and essence of ESG rating. Good information disclosure is conducive to providing more effective and comparable information for ESG rating, promoting the improvement of rating quality, and then helping investment decisions, thereby guiding capital to enterprises with good ESG performance, encouraging enterprises to improve ESG governance, and forming a positive cycle.
II. Analysis of ESG information disclosure and rating performance of mandatory disclosure sample companies
CCXGF uses the sample companies within the mandatory disclosure scope of the "Guidelines" of the three major exchanges as the statistical scope, and based on its own ESG rating model, analyzes the current status of ESG information disclosure and ESG rating performance of the mandatory disclosure sample companies. It more intuitively displays the current ESG development of my country's listed companies and the practical basis for the implementation of the guidelines, and provides a reference for future listed companies and even other corporate entities to carry out ESG information disclosure and ESG system construction.
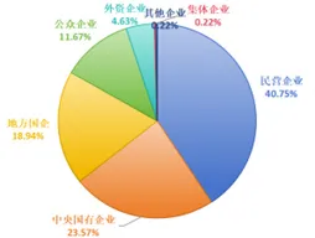
According to Wind data statistics, as of the end of June 2024, there are a total of 454 sample companies that are required to disclose during the reporting period (excluding duplicate companies within the scope of mandatory disclosure). These 454 companies belong to 30 industries (Shenwan industry classification) sectors, and the top five industries such as pharmaceuticals and biology, electronics, power equipment, non-bank finance and computer industries account for 46.92%, and the top ten industries account for more than two-thirds of all sample companies; in addition, among the 454 listed companies, central enterprises, local state-owned enterprises and private enterprises account for the highest proportion, of which central enterprises and local state-owned enterprises account for a total of 42.51%, and private enterprises account for 40.75%, which is equivalent. See the figure below for details.
Figure 1: Industry distribution of sample companies with mandatory disclosure
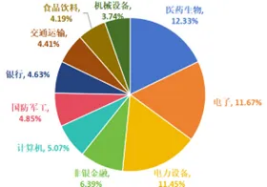
Figure 2: Distribution of attributes of sample companies subject to mandatory disclosure
(I) The proportion of ESG information disclosure is much higher than the average level of listed companies, and ESG reports are still the mainstream disclosure form
Driven by the "dual carbon" goals, listed companies' awareness of sustainable development continues to improve. Driven by both the market and regulation, more and more listed companies have taken the initiative to increase their willingness to release sustainability information. As of the end of June 2024, 45 companies in the mandatory disclosure sample have not yet published their 2024 sustainable development reports (including ESG reports, sustainable development reports, social responsibility reports, etc.), with a disclosure ratio of 90.09%, more than twice the average level of A-share listed companies. See the figure below for details.
Figure 3 Comparison of the disclosure ratio of sustainability-related reports by mandatory disclosure sample companies and A-share listed companies
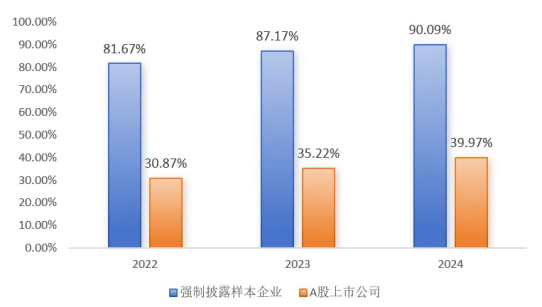
From the perspective of each sample type, in 2024, the Shenzhen Component 100 Index and companies listed simultaneously at home and abroad achieved a sustainable development report disclosure rate of 100.00%, the disclosure rate of listed companies in the Science and Technology Innovation 50 Index and the Shanghai 180 Index exceeded 90.00%, and the disclosure rate of ChiNext Index samples was nearly 70%. The mandatory disclosure sample companies showed a good understanding and practice of ESG.
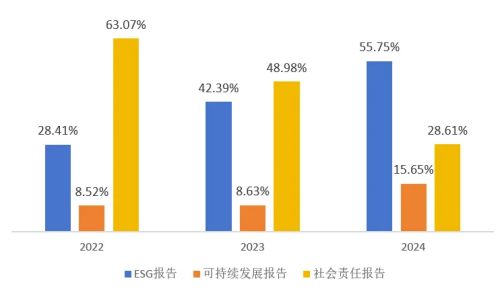
Judging from the disclosure report situation, the mandatory disclosure sample companies have undergone a major change in the form of sustainable information disclosure in 2024. In 2023, social responsibility reports accounted for 48.98%, while in 2024, ESG reports climbed to 55.75%, becoming the preferred mode for companies to communicate sustainable development information to the outside world. See the figure below for details.
Figure 4: Disclosure forms of sustainability-related reports of sample companies with mandatory disclosure
(II) The overall ESG rating performance is at the leading level among listed companies, showing a good leading and exemplary role
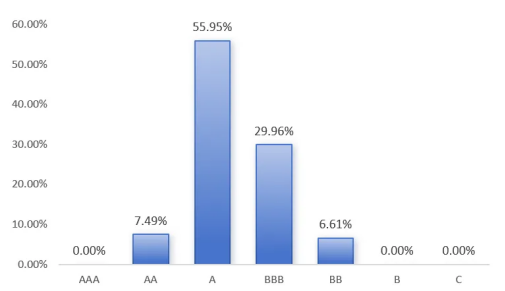
CCXGF conducted ESG ratings on 454 mandatory disclosure sample companies based on the industry ESG rating model. In the past three years, the ESG rating performance of mandatory disclosure sample companies has steadily improved, from 79.03% in 2022 to 93.39% in 2024. Specifically, there are 136 BBB-rated companies, accounting for 29.96% of the total; and there are as many as 254 companies with A-rated ratings, accounting for as high as 55.95%, which is better than the overall performance of the A-share and Chinese Hong Kong-listed stocks in 2023 (A and above account for about 12.70%). The overall ESG risk and opportunity management level of the mandatory disclosure sample companies is showing a good trend.
Figure 5: ESG performance level distribution of sample companies subject to mandatory disclosure in 2024
Judging from the performance of ESG rating results, under the guidance of the country's "dual carbon" goals, the mandatory disclosure sample companies are actively responding to the call of the ESG (environment, society and governance) concept and entering a new stage of high-quality development. Companies not only internalize ESG principles as the core requirements of corporate management, but also demonstrate their profound sense of social responsibility through multi-dimensional actions such as regularly publishing ESG reports, strengthening information transparency, ensuring production safety, promoting technological innovation, actively participating in public welfare activities, and protecting the legitimate rights and interests of employees.
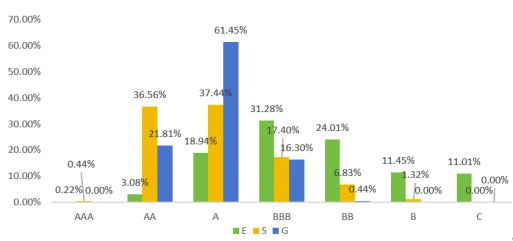
Looking at the dimensions, the environmental (E) dimension of the mandatory disclosure sample companies is concentrated in the BBB and BB levels, accounting for a total of 55.29%; the social (S) and governance (G) dimensions are mainly concentrated in the AA and A levels, accounting for 74.00% and 83.26% respectively. The performance of the environmental dimension is still the main direction that Chinese companies need to further improve at the current stage. Especially under the trend of mandatory regulatory information disclosure, the quantitative information disclosure of the environmental dimension needs to be further improved and also faces greater challenges.
Figure 6: ESG level distribution of sample companies subject to mandatory disclosure by dimension in 2024
III. Recommendations for corporate ESG information disclosure under a strong regulatory environment
The official release of the "Guidelines" fills the gap in ESG information disclosure standards at the regulatory level for listed companies in my country. It will promote the comprehensiveness, completeness, comparability and accuracy of sustainable information disclosure by listed companies, and has important guiding significance for listed companies to practice sustainable development. It also lays the foundation for the subsequent expansion of the scope of mandatory disclosure and for relevant departments to do a good job in ESG rating, index development and investment.
1. ESG information disclosure is an important task for Chinese companies going global, and they should be actively prepared in advance
As a common topic of global dialogue, the development of ESG has attracted the attention of global institutions. For Chinese companies, especially those with global business layout, paying attention to ESG, understanding ESG and managing ESG have become an important task that affects the development of corporate business. The basic framework and logic of the "Guidelines" and "Basic Standards" are consistent with the international mainstream ESG information disclosure framework, providing companies with a set of internationally forward-looking ESG information disclosure frameworks, which will help Chinese companies connect with the international environment and expand their business. It has become a basic homework that must be done by overseas companies, and they should improve their ESG information disclosure capabilities under the guidance of the "Guidelines".
(II) Accelerate the process of ESG information disclosure by taking industry-leading benchmark companies as reference
The Guidelines clearly arrange the time and content of ESG information disclosure for sample companies that are subject to mandatory disclosure. From the above analysis, it can be seen that sample companies have achieved certain results in ESG awareness and practice, but information disclosure still faces new challenges under the requirements of the Guidelines, and it takes time to improve. Sample companies should fully learn from the experience of outstanding companies in the industry, accelerate their own construction in ESG management, and make arrangements as early as possible according to the disclosure schedule to calmly respond to the information disclosure requirements in 2026. At the same time, under the dual policy influence at the national and regulatory levels, combined with the national "dual carbon" strategic time node, sample companies that have not yet been included in the mandatory disclosure should also actively pay attention to the latest requirements for ESG information disclosure, and achieve valuable disclosure in both form and substance.
(III) Based on the actual development of the enterprise itself, gradually formulate a path for building an ESG system in accordance with the development stage of the enterprise
The construction of ESG management system is a long-term work. ESG information disclosure is the first step in the construction of ESG management system of enterprises, which reflects the norms and compliance of enterprises in internal management. It is recommended to follow the principle of "from simple to complex, from form to substance", combine the different development stages of enterprises, and gradually carry out in stages, while making good cost budgets. Through cultivating sustainable development culture, establishing and improving governance structure, building information collection system, integrating into enterprise development strategy and other series of work, it will be gradually carried out. Data collection is the first step in ESG information disclosure and management. Combined with the current shortcomings of Chinese enterprises in information collection, enterprises should give priority to it. Article 8 of the draft of the Ministry of Finance's "Basic Principles" for comments mentioned that "enterprises should establish and improve systems such as data collection, verification, analysis, utilization and reporting related to sustainable information disclosure, improve internal control of sustainable information disclosure, and ensure the quality of sustainable information disclosure". In the actual implementation process, data collection work can be fully considered in terms of enterprise scale and development stage. For large enterprises, due to complex organizational structure and extensive business coverage, manual information collection is difficult and difficult to trace back, so systematic construction is a necessary choice.
(IV) Strengthen communication among various entities in the ESG ecosystem, further integrate ESG development with the internal and external environment and the actual business strategy of enterprises, and build a good ESG development ecosystem
In the process of ESG management practice, enterprises should strengthen communication with investment institutions, ESG rating agencies and other institutions, pay attention to the ESG needs of stakeholders and their own ESG rating performance, and continue to attract the attention of financial institutions and outstanding investors. As an important link between enterprises and investors, ESG ratings can provide investors with more intuitive ESG rating performance through the professionalism of third parties, which is easy to use and manage. Under the guidance of strong regulatory policies, enterprises can more effectively benchmark the content of ESG ratings by strengthening their own ESG information disclosure, and then continue to obtain more objective and scientific evaluations from third-party rating agencies, which will help enterprises better demonstrate their strength to stakeholders, and promote the high-quality development of enterprises through a virtuous cycle of the ESG ecosystem.






